Running any API with bash scripts¶
You may want to run your API using something other than Flask or plumber. To
enable this, Faculty contains the Custom API option. When specifying a
custom API, you simply need to provide an executable (for instance, a shell
script) that runs your API. If you use a shell script, make sure your script
starts the API wit exec to avoid leaving orphaned processes.
Contents
Running an API from node.js with express¶
Creating a node.js environment¶
If you want to run an API with node.js, you will need to first create an
Environment that installs node.js.
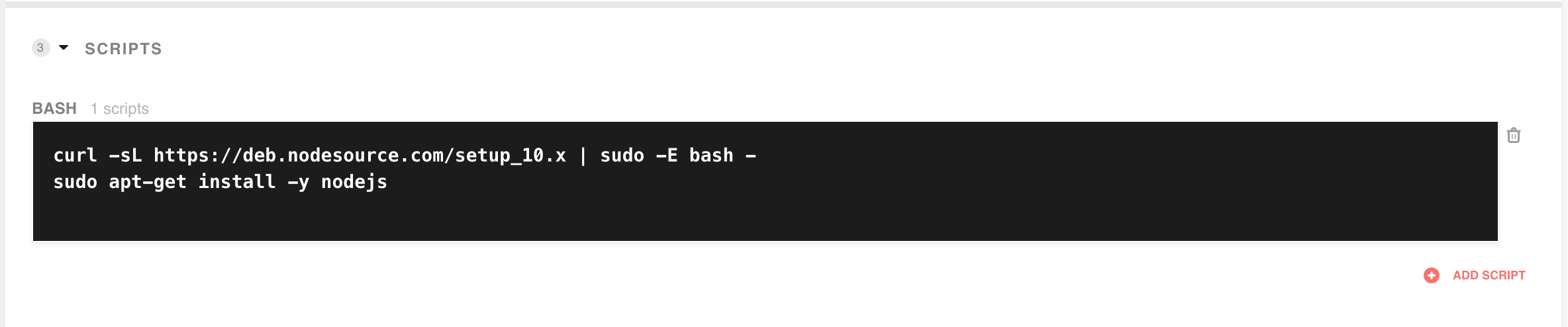
To do so, open the Enivorenments interface and add the following commands to the scripts section at the bottom:
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_10.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
Note
While installing node directly from source is the quickest way to get set up, you will often want more flexibility. For this, we recommend installing nvm).
Your environment should look like this:
In addition, our application will need two libraries: express, a web
server, and body-parser to parse JSON request bodies.
To install them, start a server with the nodejs environment in your project
(any server type) and run the following commands in a terminal:
npm init
# accept the default parameters
npm install --save express body-parser
Writing a node.js API¶
Now we need to create our actual API code. For this example, we will save the
following code to /project/api.js:
// api.js
const express = require('express')
const app = express();
const port = 8000;
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
app.use(bodyParser.json());
const catPeople = ['Schrodinger', 'Schrödinger', 'Schroedinger'];
app.post('/predict', function (req, res) {
const { lastName } = req.body;
const mostLikely = catPeople.includes(lastName) ? 'cat' : 'dog';
const payload = { mostLikely };
res.status(200).send(payload);
});
console.log(`==> API listening on port ${port}`)
app.listen(port);
Note that the API needs to listen on port 8000.
Note
See the Express tutorial for a more in-depth tutorial on writing APIs with NodeJS and Express.
The last thing we need to do before we test our API is to create the bash
script that runs the API. This only needs to contain one command. We will save
this to /project/run.sh
#!/bin/bash
exec nodejs api.js
Once we have these components, we can create the API in the Faculty Deployment interface.
Configuring a custom API¶
Go to the Deployments page for your project in Faculty and create a new API.
You will be asked to choose a name, a domain name and a type for your API. For
type, choose Custom. Your domain name needs to be unique across all of
Faculty. I suggest a domain name like cats-vs-dogs-2118, where you
replace 2118 with a random string of your choice.
In the API settings page, leave the working directory as /project, and set
the script to /project/run.sh. From the Environments dropdown, select the
node.js environment we created earlier.

After you have your API set up, you can test and ultimately deploy it. Head to Test your API to find out how to go about the testing process.